You have just placed a deposit for your new home and need to decide on a Mortgage Loan package now. So, what are the types of Floating Interest Bank Rate that are commonly offered by the bank. So, just to recap, what is a Floating Interest Bank Rate? It’s an underlying index plus the spread that the bank is getting and, that will be the interest rate that you are paying for the year.
An example of some of the interest rate that is currently offered by the bank; a one-month SIBOR, three or six-month SIBOR or, their Fixed Deposit Rate to be the underlying index as well. The spread that the bank is offering you tends to get higher as the years go by. For example, you can see one-month SIBOR plus 0.35% for year one, 0.45% for year two, and thereafter 0.6%.
The first type of Floating Interest Bank Rate will be the Bank’s Board Rate. As the name suggests, it’s a board rate that is derived by the bank to determine what is the Mortgage Interest Rate. This is one of the most common and traditional methods adopted by the bank to derive your Mortgage Interest Rate. The popularity actually declined with the recent introduction of SIBOR and Fixed Deposit Pegged Interest Rate. One of the main advantages of a Bank’s Board Rate is, it’s unlikely to change too frequently. Today, if you were to take up a Mortgage Loan with one of the banks and they stipulate that the Bank’s Board Rate is at 2.5. How will it look, if they were to increase the rate very frequently, say from 2.5 all the way to 2.7, 2.8, 2.9? This will actually result in the loss of confidence among its clients.
Therefore, banks will not usually change their rates too frequently so as to maintain the confidence level among their clients and, of course, the disadvantage of a Bank’s Board Rate is there is no transparency because this is a rate that is derived from the bank and it is used to determine your interest rate. There is no reference or any information that you can get because it is at the discretion of the bank to review the rate and increase or decrease accordingly as and when it is needed.

Source : abs.org.sg, 15 May 2020 SIBOR / SOR Rates
Moving on to the next type of Floating Interest Bank Rate. This is most commonly utilised by the banks – the SIBOR and SOR rate. SIBOR is known as the Singapore Interbank Offer Rate. It’s the rate that the banks lend money to one another. SOR will be your Swap Offer Rate. It’s pretty much similar to your Singapore Interbank Offer Rate, just that there is another underlying exchange between your Singapore Currency and the US Currency.
Of course, one of the advantages of a SIBOR and SOR Pegged Rate is it allows the bank to keep the spread competitive because it is very transparent. Here is the link for the current SIBOR and SOR rate.

The main disadvantage of a SIBOR and SOR Pegged Rate is it’s very volatile. Your interest rate fluctuates according to market environment.
SIBOR
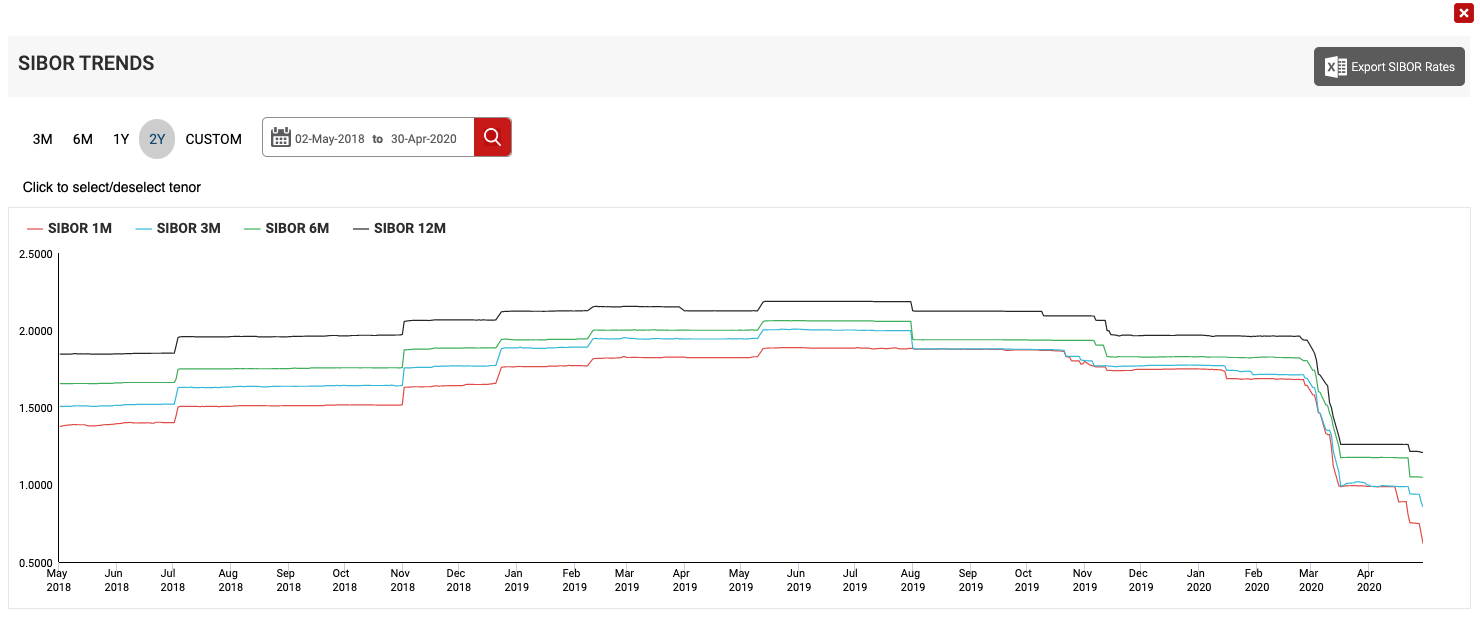
(Source : abs.org.sg , 2year SIBOR Trends)
Just to give you an example, two years back, let’s say three months SIBOR was about 0.99 percent and now it has went up 1.98 percent. That’s almost a 100 percent increase in the SIBOR rate. If your Mortgage Loan is pegged to a three months SIBOR, you are effectively paying 100 percent more than what you are paying two years back.
SOR
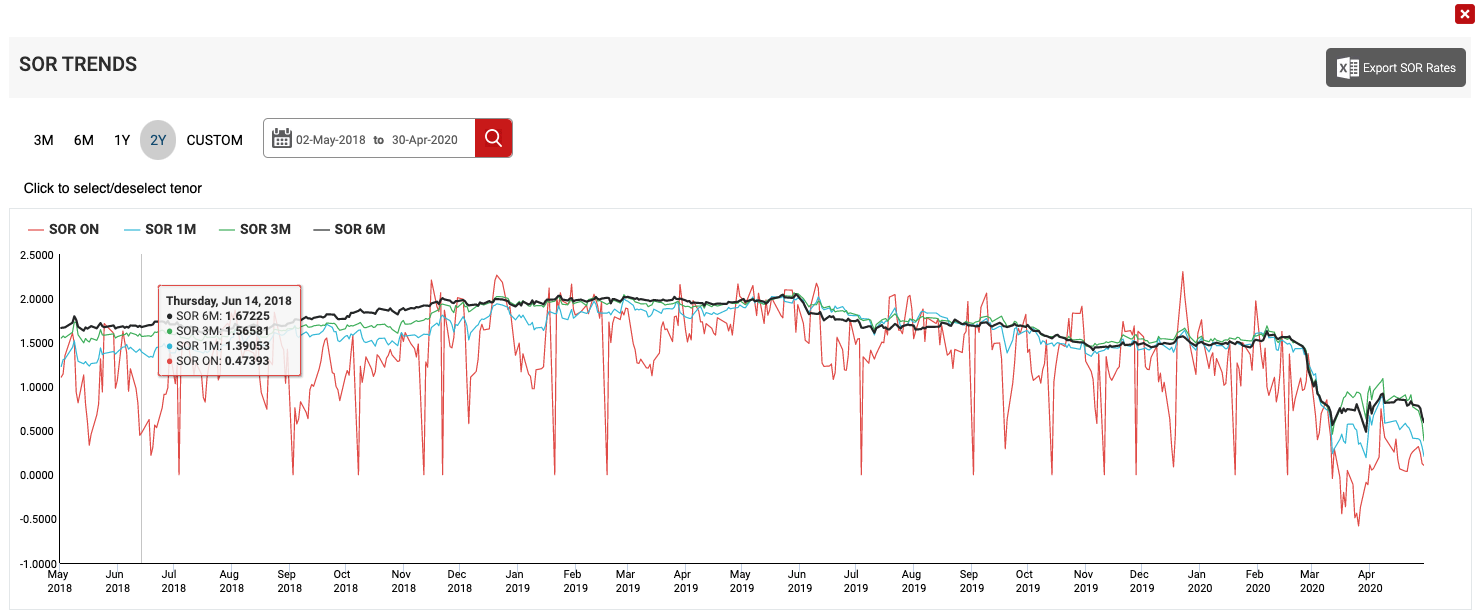
(Source : abs.org.sg , 2year SOR Trends)
Moving on to the SOR rates. This is actually similar to SIBOR and pegged to the currency exchange rate between the US and Singapore dollars. It’s definitely much more volatile and in recent times, banks have stopped adopting SOR rate because of its volatility.
Fixed Deposit Linked Rates
The last type of Floating Interest Bank Rate will be the Fixed Deposit Linked Rate. This is actually pegged to a bank’s Fixed Deposit Rate. It could be for six months Fixed Deposit, eight months Fixed Deposit as the underlying index and, the advantage of having a Fixed Deposit Pegged Interest Rate is it is transparent. The rates are all being published by the various banks in terms of what is the current interest rate they’re offering for their Fixed Deposit. There is the disadvantage because it is ultimately still determined by the bank and, they have the sole discretion to adjust the rates accordingly.
I hope this episode has helped you in gaining a better understanding of the different types of Floating Interest Rate offered by the banks.
See you in the next one!







